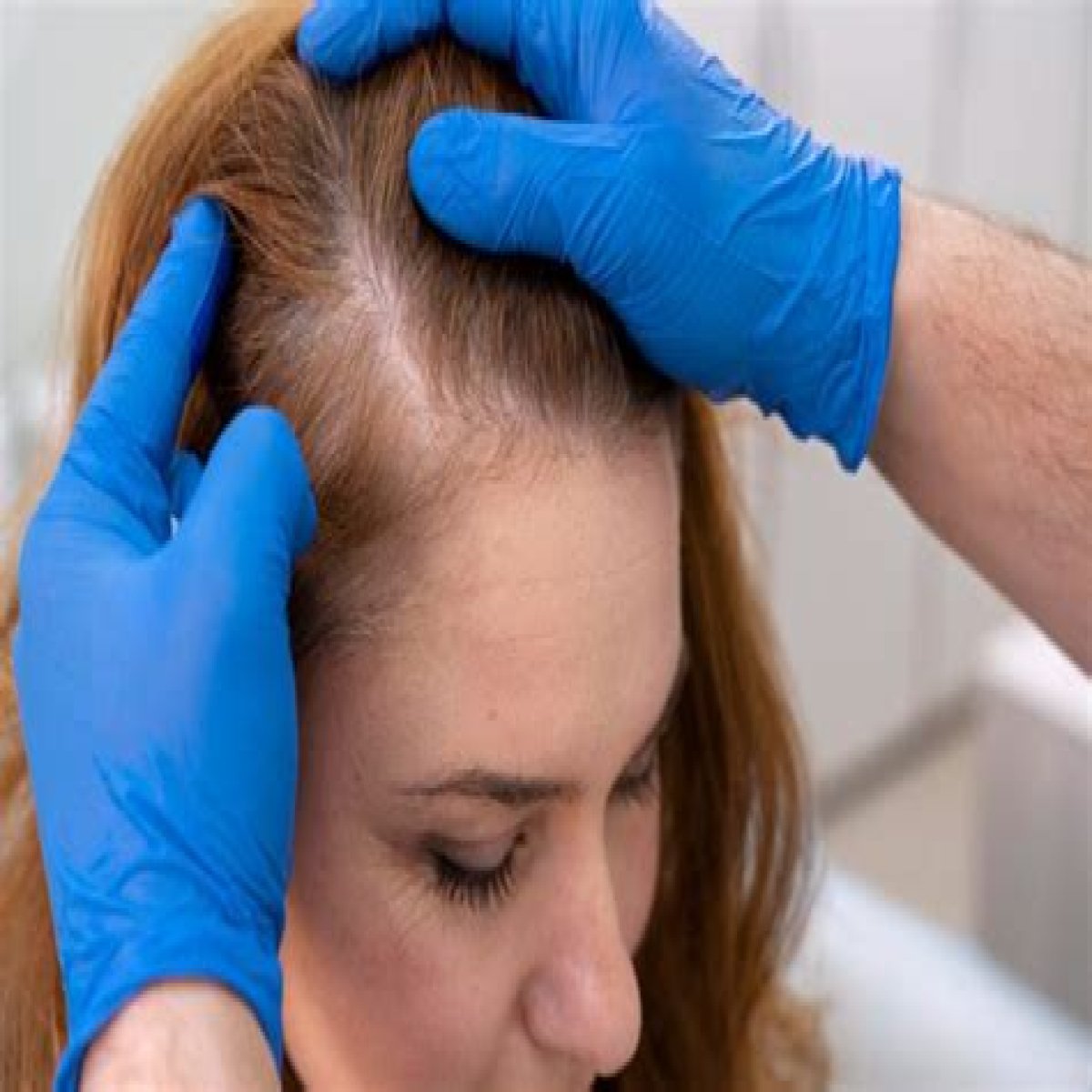
Light thinning refers to the early stages of hair loss, where the hair appears thinner and less dense than usual. Progressed thinning, on the other hand, is a more advanced stage of hair loss, where the hair becomes significantly thinner and the scalp becomes more visible.
Light thinning is a common condition that affects both men and women. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Progressed thinning is a more serious condition that can lead to baldness if left untreated.
There are a number of treatments available for light thinning and progressed thinning. These treatments can help to slow down or stop hair loss, and in some cases, they can even help to regrow hair.
Light Thinning vs Progressed Thinning
Light thinning and progressed thinning are two stages of hair loss that can affect both men and women. Light thinning is the early stage of hair loss, where the hair appears thinner and less dense than usual. Progressed thinning is a more advanced stage of hair loss, where the hair becomes significantly thinner and the scalp becomes more visible.
- Causes: Light thinning can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Progressed thinning is typically caused by androgenetic alopecia, a genetic condition that leads to hair loss.
- Symptoms: Light thinning is characterized by a gradual thinning of the hair, while progressed thinning is characterized by more significant hair loss and a visible scalp.
- Treatment: There are a number of treatments available for light thinning and progressed thinning, including topical medications, oral medications, and surgery.
- Prevention: There is no sure way to prevent light thinning or progressed thinning, but there are some things that can be done to reduce the risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress.
- Outlook: Light thinning and progressed thinning are both treatable conditions. With early diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to slow down or stop hair loss and even regrow hair.
Light thinning and progressed thinning are two common conditions that can affect both men and women. While light thinning is typically not a cause for concern, progressed thinning can lead to baldness if left untreated. If you are concerned about hair loss, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause and get the appropriate treatment.
Causes
Light thinning and progressed thinning are two stages of hair loss that can be caused by a variety of factors. Light thinning is typically caused by genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions, while progressed thinning is typically caused by androgenetic alopecia, a genetic condition that leads to hair loss.
Understanding the causes of light thinning and progressed thinning is important for developing effective treatment plans. For example, if light thinning is caused by a medical condition, treating the underlying condition may help to slow down or stop hair loss. Similarly, if progressed thinning is caused by androgenetic alopecia, there are a number of treatments available that can help to slow down or stop hair loss and even regrow hair.
If you are concerned about hair loss, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause and get the appropriate treatment.
Symptoms
The difference in symptoms between light thinning and progressed thinning is a key factor in distinguishing between the two conditions. Light thinning is characterized by a gradual thinning of the hair, which may be noticeable when styling or combing the hair, but is not always immediately obvious to others. Progressed thinning, on the other hand, is characterized by more significant hair loss and a visible scalp. This can be a cause of concern for many people, as it can affect their appearance and self-confidence.
- Early Detection: The difference in symptoms between light thinning and progressed thinning highlights the importance of early detection and treatment for hair loss. If you are concerned about hair loss, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause and get the appropriate treatment. Early treatment can help to slow down or stop hair loss and even regrow hair.
- Treatment Options: The difference in symptoms between light thinning and progressed thinning also affects the treatment options available. For light thinning, there are a number of topical and oral medications that can help to slow down or stop hair loss. For progressed thinning, there are a number of surgical and non-surgical treatments available that can help to restore hair growth.
Understanding the difference in symptoms between light thinning and progressed thinning is important for developing effective treatment plans and managing expectations. If you are concerned about hair loss, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause and get the appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Understanding the different treatments available for light thinning and progressed thinning is crucial in addressing hair loss effectively. Treatments aim to slow down or stop hair loss, and in some cases, even regrow hair. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of hair loss and the underlying cause.
- Topical Medications: Topical medications, such as minoxidil and finasteride, are applied directly to the scalp. They work by stimulating hair growth and preventing further hair loss.
- Oral Medications: Oral medications, such as finasteride and dutasteride, are taken by mouth. They work by blocking the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair loss.
- Surgery: Surgery is an option for people with more advanced hair loss. Surgical procedures, such as hair transplantation and scalp reduction, can restore hair growth and improve the appearance of the scalp.
It's important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for light thinning or progressed thinning. Early intervention and adherence to treatment can improve outcomes and prevent further hair loss.
Prevention
Understanding the preventive measures for light thinning and progressed thinning is crucial for proactive hair care. While there is no guaranteed way to prevent hair loss, adopting a healthy lifestyle can minimize the risk and promote overall hair health.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, such as vitamins A, C, D, and E, is vital for hair growth and scalp health. These nutrients nourish the hair follicles and support the production of healthy hair.
- Regular Exercise: Exercise promotes blood circulation, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the hair follicles. Regular physical activity can improve hair growth and reduce stress levels, which can contribute to hair loss.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can trigger hair loss. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature, can help manage stress levels and promote hair health.
In the context of light thinning vs progressed thinning, prevention plays a significant role. By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing more advanced stages of hair loss and maintain healthier hair.
Outlook
In the context of light thinning vs progressed thinning, the outlook is generally positive, as both conditions are treatable. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively manage hair loss and potentially regrow hair.
- Early Intervention: Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for successful treatment outcomes. Seeking professional advice at the onset of hair loss allows for prompt identification of the underlying cause and initiation of appropriate treatment. This proactive approach increases the chances of slowing down or stopping hair loss and promoting hair regrowth.
- Treatment Options: There are various treatment options available for light thinning and progressed thinning, ranging from topical medications to oral medications and surgical procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of hair loss and the individual's specific needs. With advancements in hair restoration techniques, effective treatments are available to address different stages of hair loss.
- Realistic Expectations: While treatments can be effective in managing hair loss, it is essential to have realistic expectations. Hair regrowth may not always be possible, and the results can vary depending on individual factors. Open communication with healthcare providers and realistic expectations can help patients make informed decisions and cope with the challenges of hair loss.
- Ongoing Management: Hair loss treatment often requires ongoing management and maintenance. Regular follow-up appointments and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for sustained results. This ongoing care ensures that hair loss is effectively controlled and any potential setbacks are promptly addressed.
Overall, the outlook for light thinning and progressed thinning is positive, provided there is early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and ongoing management. By understanding the available options and maintaining realistic expectations, individuals can effectively address hair loss and improve their overall well-being.
FAQs on Light Thinning vs Progressed Thinning
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding light thinning and progressed thinning, providing informative answers to enhance understanding of these hair loss conditions.
Question 1: What are the key differences between light thinning and progressed thinning?
Light thinning refers to the early stages of hair loss, characterized by a gradual reduction in hair density. Progressed thinning, on the other hand, represents a more advanced stage where hair loss becomes more noticeable, with significant thinning and increased scalp visibility.
Question 2: What are the common causes of light thinning and progressed thinning?
Light thinning can result from various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Progressed thinning is often associated with androgenetic alopecia, a genetic condition that leads to hair loss.
Question 3: Are there effective treatments for light thinning and progressed thinning?
Yes, there are various treatment options available for both light thinning and progressed thinning. These include topical medications, oral medications, and surgical procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of hair loss and the underlying cause.
Question 4: Can light thinning progress to progressed thinning?
Yes, light thinning can progress to progressed thinning if left untreated. However, early diagnosis and intervention can help slow down or stop the progression of hair loss.
Question 5: Is it possible to prevent light thinning and progressed thinning?
There is no guaranteed way to prevent hair loss, but adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, may reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
Question 6: What is the outlook for individuals with light thinning or progressed thinning?
With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the outlook for individuals with light thinning or progressed thinning is generally positive. Treatment can help slow down or stop hair loss and potentially regrow hair.
Understanding the differences, causes, and treatments for light thinning and progressed thinning empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their hair care and seek professional advice when necessary.
Tips on Managing Light Thinning vs Progressed Thinning
Understanding the differences between light thinning and progressed thinning is crucial for developing effective hair care strategies. Here are some informative tips to help manage these conditions:
Tip 1: Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection of hair loss is essential. If you notice signs of light thinning, such as gradual hair loss or reduced hair density, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early intervention can help slow down or stop hair loss and improve treatment outcomes.
Tip 2: Identify the Underlying Cause
Determining the underlying cause of hair loss is essential for effective treatment. Consult a dermatologist or trichologist to identify any underlying medical conditions or genetic factors contributing to hair thinning or loss.
Tip 3: Explore Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available for light thinning and progressed thinning, including topical medications, oral medications, and surgical procedures. Discuss the available options with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on your individual needs.
Tip 4: Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support overall hair health and minimize the risk of hair loss. Ensure a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, engage in regular exercise, and manage stress levels to promote hair growth and scalp health.
Tip 5: Be Patient and Consistent
Hair loss treatment often requires patience and consistency. Adhere to your treatment plan as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Results may not be immediately noticeable, but with patience and consistency, you can improve hair health and potentially regrow hair.
Tip 6: Manage Expectations
It is essential to have realistic expectations regarding hair loss treatment. While treatments can be effective, hair regrowth may not always be possible. Discuss realistic goals with your healthcare provider to avoid disappointment and maintain a positive outlook.
Tip 7: Seek Professional Advice
If you are concerned about hair loss, do not hesitate to seek professional advice. Consult a dermatologist or trichologist who specializes in hair loss treatment. They can provide personalized guidance, recommend appropriate treatments, and help you manage hair loss effectively.
By following these tips, you can proactively manage light thinning or progressed thinning, improve hair health, and maintain a healthy head of hair.
Remember, early detection, appropriate treatment, and consistent hair care are essential for successful hair loss management.
Conclusion
In summary, light thinning and progressed thinning represent different stages of hair loss with varying causes and treatments. Understanding the distinctions between these conditions is paramount for effective hair care and management.
Early detection and intervention are crucial for successful hair loss treatment. Identifying the underlying cause and exploring appropriate treatment options can help slow down or stop hair loss and potentially regrow hair. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing stress contribute to overall hair health and reduce the risk of hair loss.
Realistic expectations and patience are essential throughout the hair loss management journey. With the advancements in hair restoration techniques and the guidance of healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively address hair loss concerns and improve their hair health.
Remember, hair loss is a common condition that can be managed with the right approach. By staying informed, seeking professional advice when necessary, and adopting healthy hair care practices, we can promote hair growth and maintain a healthy head of hair.
Unveiling The Truth: Nelly's Smoking Habits RevealedUnveiling The Secrets: Fits Everybody Unlined Demi BraUnveiling The Secrets Of Crave: A 2023 Cinematic Odyssey